Name
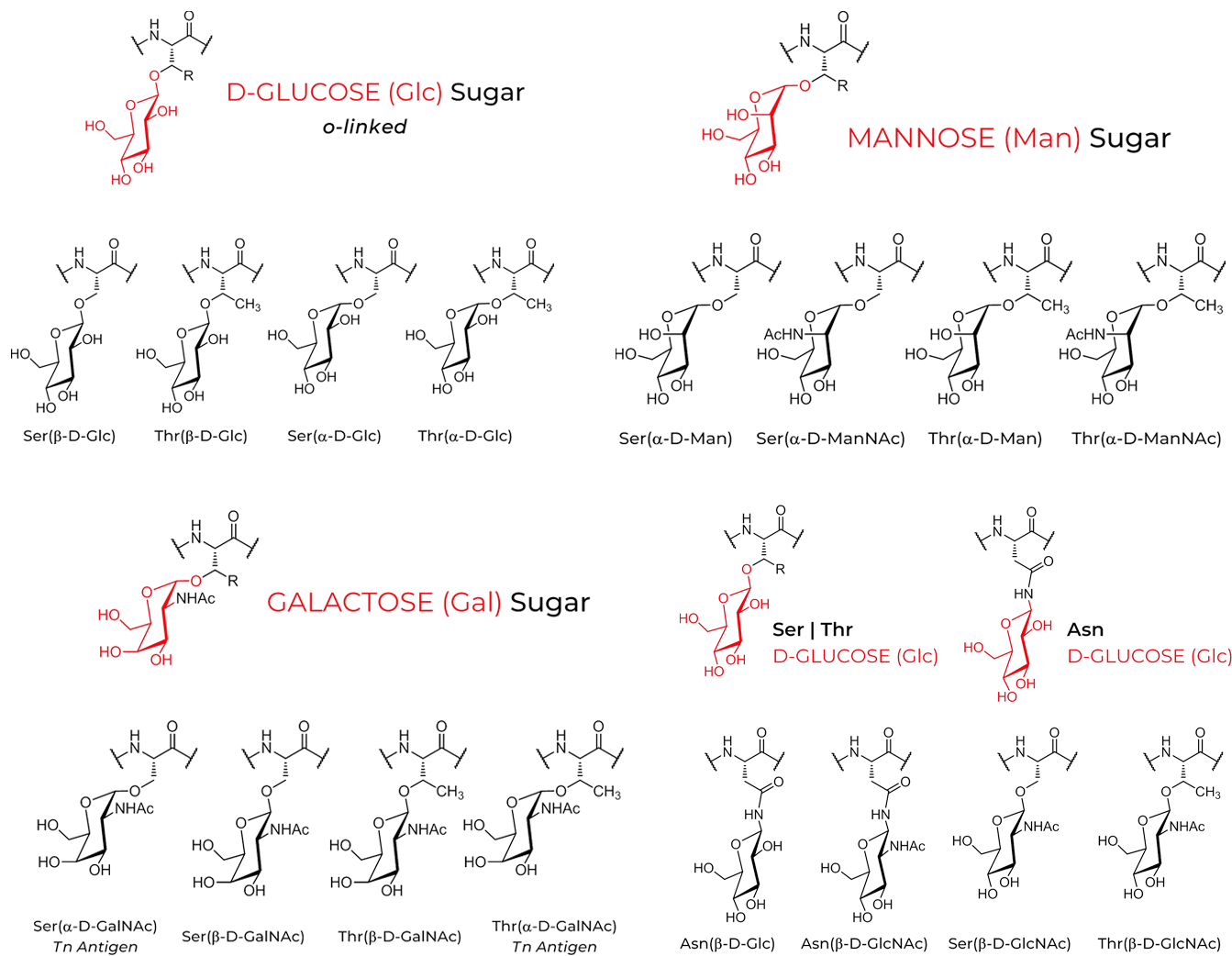
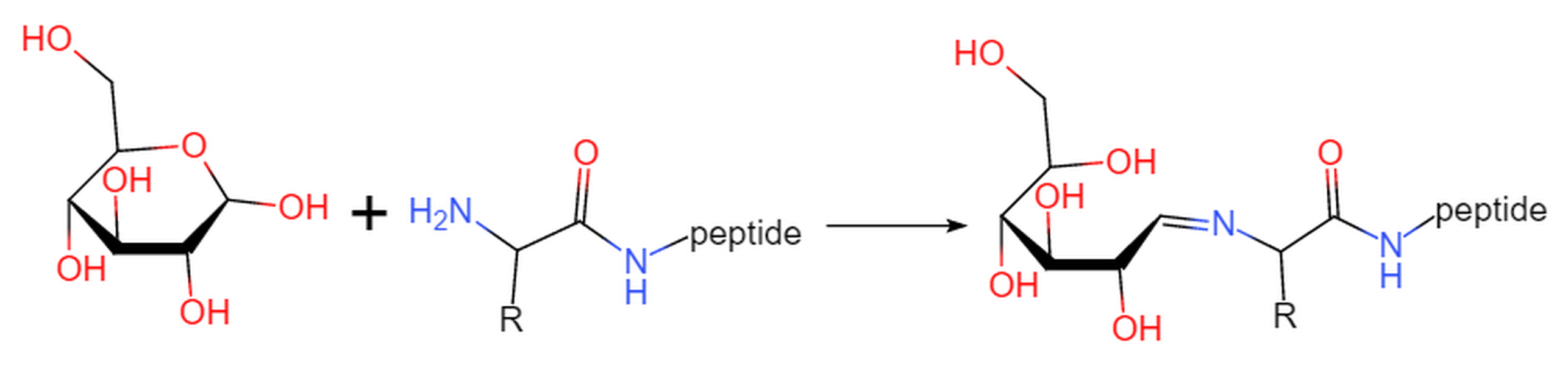
Fmoc-L-Asn((Ac)3-β-D-GlcNAc)-OH
CAS#: 131287-39-3
Fmoc-L-Ser((Ac)6-ɑ-D-Galβ(1-3)GalNAc)-OH
CAS#: 125760-30-7
Fmoc-L-Ser((Ac)3-β-D-GlcNAc)-OH
CAS#: 160067-63-0
Fmoc-L-Ser((Ac)4-β-D-Glc)-OH
CAS#: 337903-65-8
Fmoc-L-Thr((Ac)6-ɑ-D-Galβ(1-3)GalNAc)-OH
CAS#: 125760-33-0
Fmoc-L-Thr((Ac)3-β-D-GalNAc)-OH
CAS#: 133575-43-6
Fmoc-L-Thr((Ac)4-β-D-Glc)-OH
CAS#: 130548-92-4
Name
Fmoc-L-Ser((Ac)3 -β-D-xyl)-OH
CAS#: 105678-33-9
Fmoc-L-Ser((Ac)3-ɑ-D-GalNAc)-OH
CAS#: 160067-63-0
Fmoc-L-Ser((Ac)4-β-D-Gal)-OH
CAS#: 96383-44-7
Fmoc-L-Thr((Ac)3 -β-D-xyl)-OH
Fmoc-L-Thr((Ac)3-ɑ-D-GlcNAc)-OH
CAS#: 160168-40-1
Fmoc-L-Thr((Ac)4-β-D-Gal)-OH
CAS#: 127656-85-3











3-β-D-GlcNAc)-OH.png)
6-ɑ-D-Galβ(1-3)GalNAc)-OH.png)
3-β-D-GlcNAc)-OH.png)
4-β-D-Glc)-OH.png)
6-ɑ-D-Galβ(1-3)GalNAc)-OH.png)
3-β-D-GalNAc)-OH.png)
4-β-D-Glc)-OH.png)
3 -β-D-xyl)-OH.png)
3-ɑ-D-GalNAc)-OH.png)
4-β-D-Glc)-OH.png)
3 -β-D-xyl)-OH.png)
3-ɑ-D-GlcNAc)-OH.png)
4-β-D-Glc)-OH.png)




 Contact us by We-chat.
Contact us by We-chat.